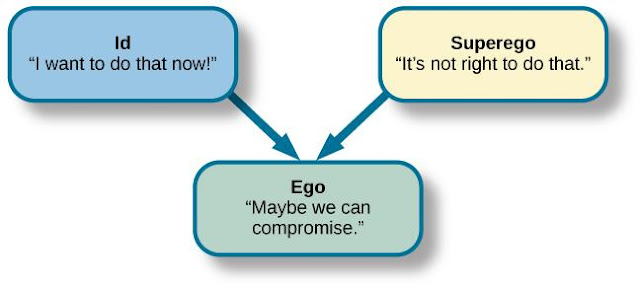
This particular theory is an psychological concept of the uncanny as something that is strangely familiar, rather than just mysterious. Freud sought to explain how the unconscious operates by proposing that it has a particular structure. He proposed that the unconscious was divided into three parts. ID , Ego and Superego. The ID is presented as the primary process of thinking - our most primitive need gratification type thoughts. The Superego is represented our conscience and counteracted the ID with moral and ethical thoughts. The Ego stands in between both to balance our primitive needs and our moral/ethical beliefs. A healthy ego provides the ability to adapt to reality and interact with the outside world in a way that accommodates both ID and Super Ego. This particular theory is therefore set in 3 different ways.
Sadistic Voyeurism
Sadistic voyeurism is watching someone without their knowledge. For example, in 1960, the film peeping tom was released and directed by Michael Powell. The film is a disturbing thriller that is about a killer who takes pictures of his victims right before murdering them. The killer aims to capture the fear of his victims on camera which is also known as sadism. The phrase peeping tom elicits the idea of someone being perverted and taking pleasure in watching other people which is also known as sadistic voyeurism
Binary Opposites - Claude Levi - Strauss
Claude Levi Strauss was a french anthropologist and ethnologist who created the concept of binary opposition. Binary opposition is a pair of related concepts that are opposite in meaning. It is also the system by which , in language and thought, two theoretical opposites are strictly defined and set off against one another. For example, evil would be the binary opposite of good. Within the media field, binary oppositions are used very frequently in films, especially in the horror genre. Many horror films include sets of binary opposites in their plots. Particularly good and evil, sane and insane and human and supernatural.
Narrative/Codes theory - Roland Barthes
Roland Barthes was a french literary theorist, philosopher, critic and semiotician which means he studied cultural signs and symbols. He explored a diverse range of fields and he influenced the development of schools. Barthes said that texts may be open or closed. Barthes codes theory consisted of 5 parts. Firstly, the enigma code refers to mystery within a text. Enigmas within the narrative make the audience want to know more and unanswered enigmas tend to frustrate the audience. The second code is the action code. This code refers to the resolution of a film and how action ensures the resolution is produced. The third code is the semantic code which refers to parts within a text that suggests or refers to additional meanings in a subliminal way. The fourth code is the symbolic code which is about symbolism within text. It exercises opposites to show contrast and create greater meaning, creating tension, drama and character development. The last code within Barthes code theory is the referential code. This means some part of a narrative can reference to other narratives and pieces of media, this is similar to intertextuality.







No comments:
Post a Comment